The Invisible Barrier Keeping Two Worlds Apart
**Wallace Line: The Ecological Boundary Between Bali and Lombok**
**Introduction**
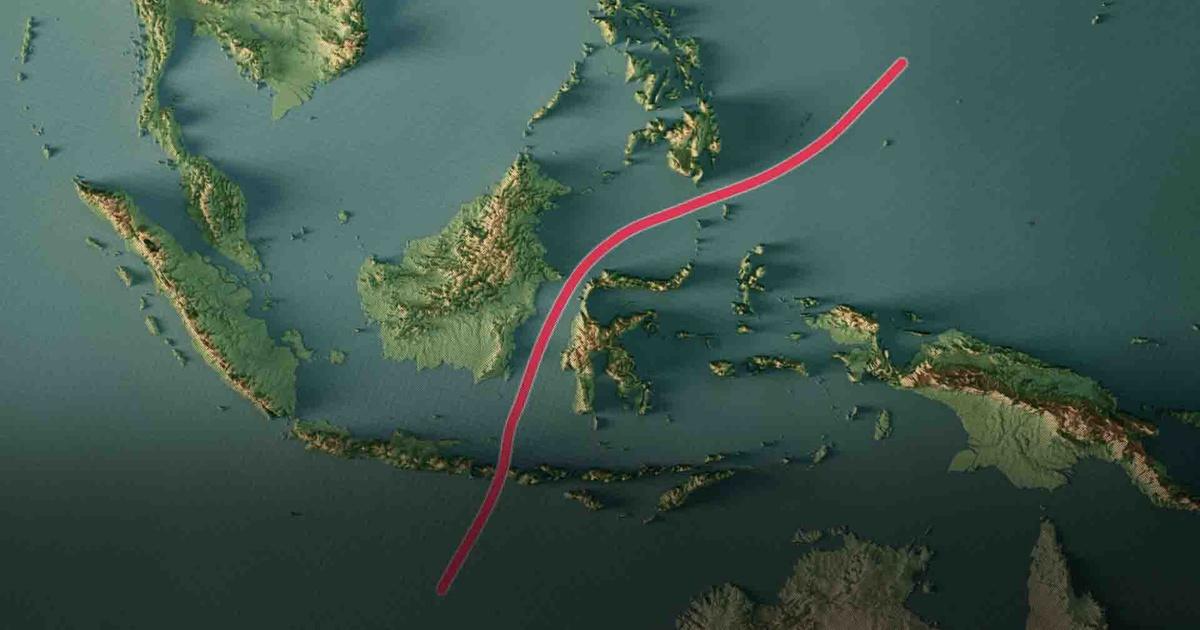
The Wallace Line, an important ecological concept, marks the biological boundary between two different animal zones in the Indonesian archipelago, specifically between the islands of Bali and Lombok. The line is approximately 32 km long and is not visible on a geographical map, but it has profound implications for understanding the distribution of animal species on Earth.
**Discovery by Alfred Russel Wallace**
Alfred Russel Wallace, a British naturalist, geographer, and anthropologist, discovered and mapped the Wallace Line during his voyage through the Malay Archipelago from 1854 to 1862. The eight-year journey is one of the most famous scientific voyages in history, resulting in many important discoveries of animals and plants.
1. **Breakthrough Observations**:
– Wallace made observations of the transfer of animal species between nearby islands and found that this transfer was not gradual but often very sudden. He noted that when traveling from Bali to Lombok, the animal species changed dramatically, from species of Asian origin to species typical of Australia.
– Wallace noted that on the west side of the Wallace Line, animals such as rhinoceroses, elephants and tigers appeared, while on the east side, animals such as Komodo dragons and many marsupials became common.
2. **Biogeography Concept**:
– Wallace was one of the pioneers in the field of biogeography. He discovered that not only were there differences between animal species, but also that geological history had a strong influence on the development of biological life.
– He speculated that the Sunda continents (including Bali, Java, and Sumatra) were once connected to each other and to the Asian continent, while the Sahul continent (including Australia and New Guinea) was a separate landmass. This explains the biological differences between the two regions.
**The Wallace Line and Geological Impact**
The Wallace Line is not only a biological boundary, but also reflects the influence of geological processes on the development of biological life. The movement of tectonic plates has created significant changes in the environment and climate, leading to the formation of the unique islands and ecosystems we see today.
– **Different Ecosystems**:
– To the west of the Wallace Line, there are many large mammals and birds, indicating the influence of Asia in biological development. Animals such as jungle fowl, monkeys, and other large mammals are often found in this area.
– To the east, the presence of Australian-specific animals such as kangaroos and large reptiles, such as the Komodo dragon, indicates the independent development of this ecosystem.
– **The Importance of Wallace’s Line**:
– Wallace’s Line has become a symbol of biodiversity and evolution. It not only reflects the distribution of animal species but also demonstrates modern ecological and biological research, emphasizing the importance of conservation and research on flora and fauna in the context of climate change.
**Conclusion**
Wallace’s Line is not only an ecological boundary but also a scientific legacy reflecting Alfred Russel Wallace’s ingenuity in observing and analyzing biodiversity. His discovery has contributed greatly to our understanding of ecosystems, evolution and geological factors affecting life on Earth. The Wallace Trail continues to be an important destination for researchers and nature lovers, helping them to explore and better understand the rich biological history of the area.








